Lithium carbonate is the basic raw material for the production of lithium compounds and metals, and a lot of lithium products are generally prepared by reacting lithium carbonate with other compounds. The commonly used preparation methods for lithium carbonate include lime sintering process, recrystallization method, causticizing process, pressure cooking process, precipitation method, etc. Among which the lime sintering process is no longer used because of its high cost; The cost of recrystallization method is low, but the effect of impurity separation is poor; The causticizing process has the advantages of simple operation, high reliability, less investment and wide application, but it cannot accurately control the end point, while the product purity and recovery rate are relatively low, resulting in higher costs. The pressure cooking process has the disadvantages of high energy consumption and high production cost, and requiring strict requirements for raw materials; Compared to other methods, the precipitation method is widely used in industry, usually using sodium carbonate as a precipitant to combine Li+ with CO32- to form lithium carbonate precipitation, which is called the lithium sedimentation process.

Lithium carbonate wet powder

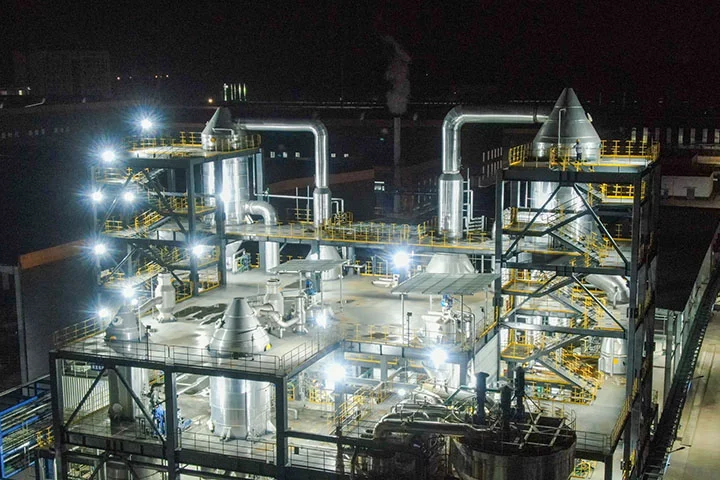
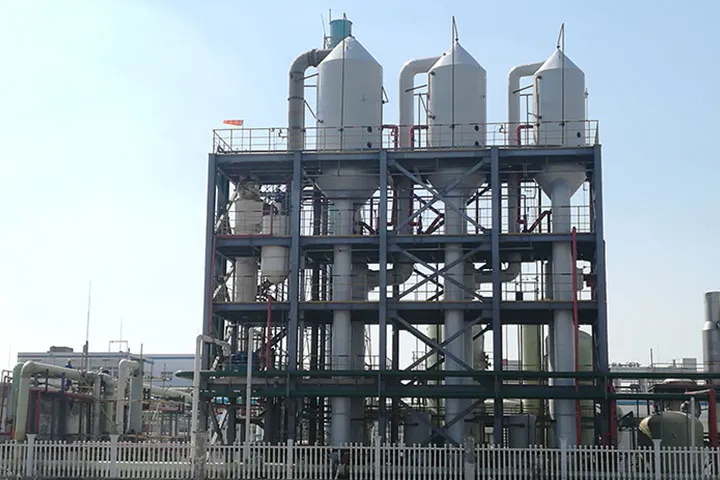
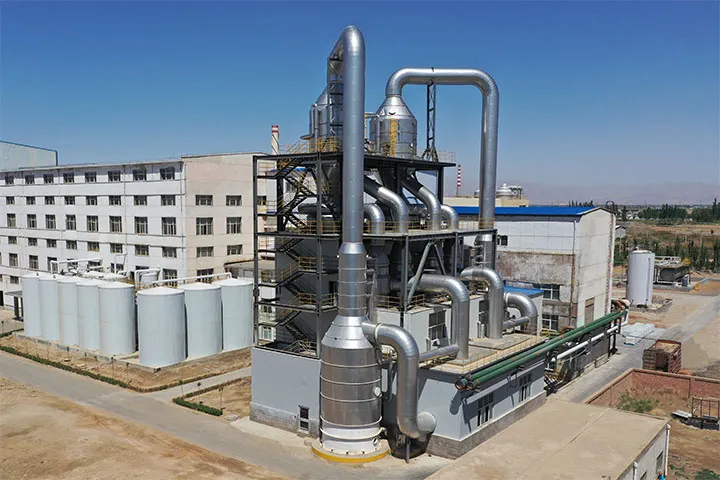
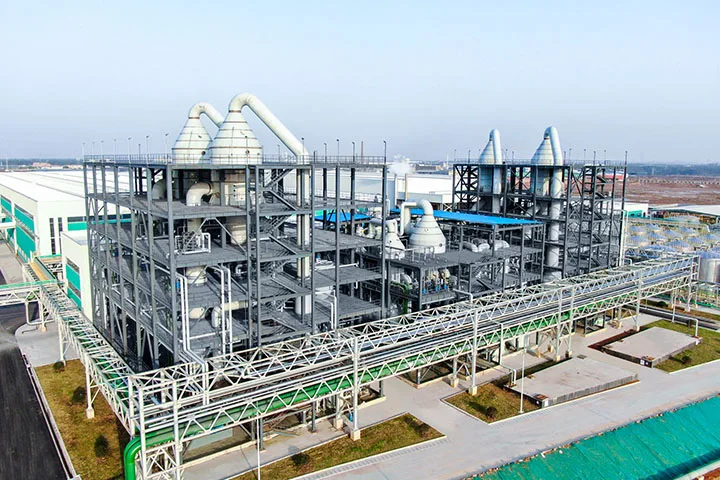
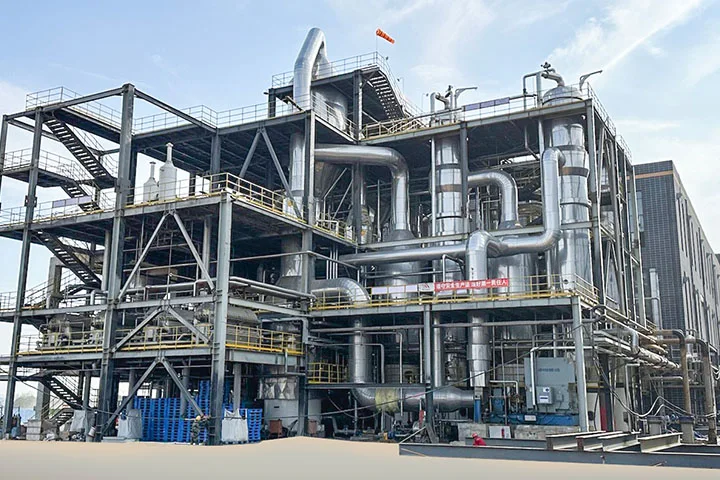
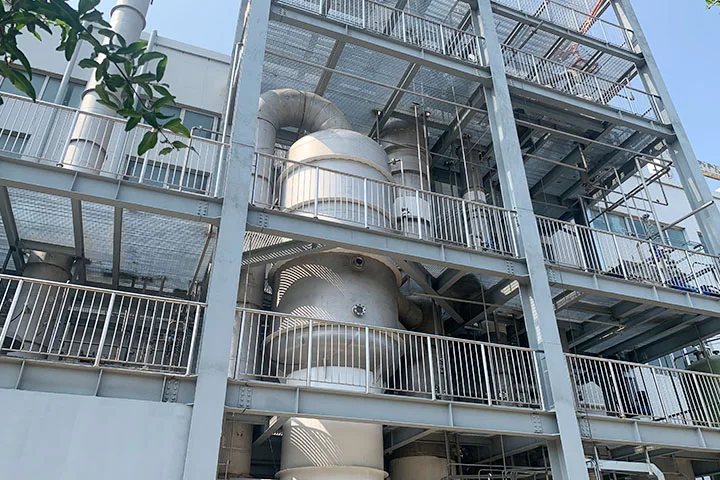
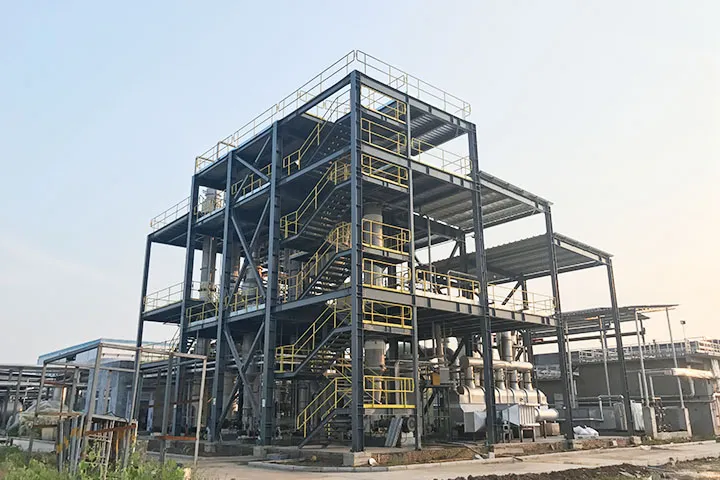
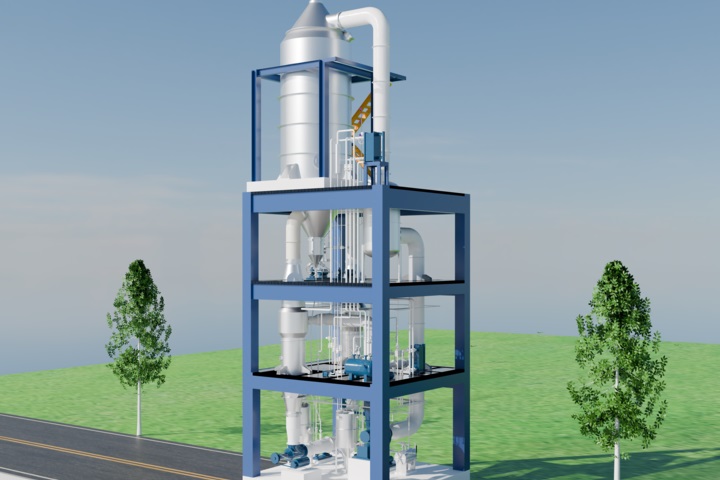
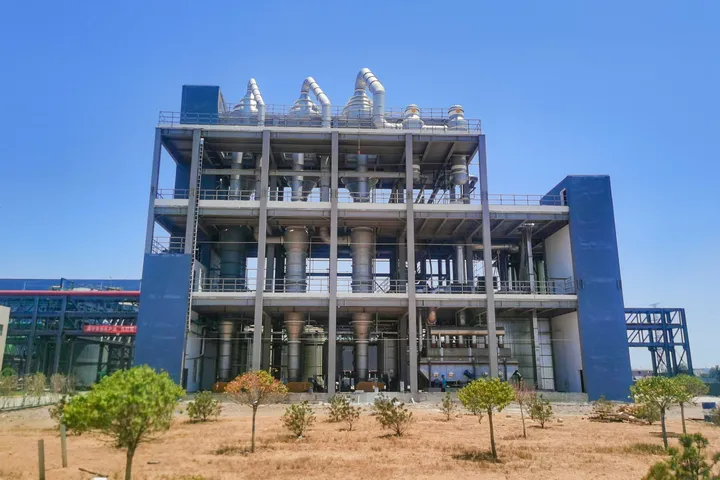
Lithium Sedimentation Reactor
The main purpose of this process is to maximize the conversion of lithium oxide into lithium carbonate products, to improve the lithium sedimentation rate, product extraction rate, and metal recovery rate, thereby reducing material consumption and lowering production costs, and ultimately ensure product quality and meet customer requirements. The specific chemical reaction formula is as follows:
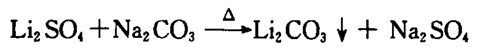
Notes in the lithium sedimentation process:
1) The temperature must meet the standard: in terms of product quality, if the temperature is not enough, the crystal form of the product cannot meet the requirements; In terms of controlling production costs, insufficient temperature and low lithium sedimentation rate result in significant losses of lithium sulfate and alkaline solution.
2) The concentration of the lithium sulfate must meet the requirements: if the concentration of the lithium sulfate is low, the output rate per unit of product will be low, but after the reaction, the concentration of CO32-and Li+ in the mother liquor remain unchanged, resulting in significant losses of the lithium sulfate and alkaline solution. On the contrary, although material with high concentration is beneficial for cost control, impurities in products with too high concentration will also increase accordingly.
3) The concentration of Li+ and CO32-in the liquid after lithium sedimentation should be as low as possible. A high concentration of Li+ indicates a low degree of extraction of lithium ions from lithium sulfate, resulting in a waste of lithium sulfate. A high concentration of CO32- indicates a high alkali consumption. However, due to the complex ion effect and solubility relationship, there will be a certain amount of Li+ and CO32- in the mother liquor. So to ensure a relatively low Li+ concentration finally, it is necessary to ensure a relatively high CO32- concentration.
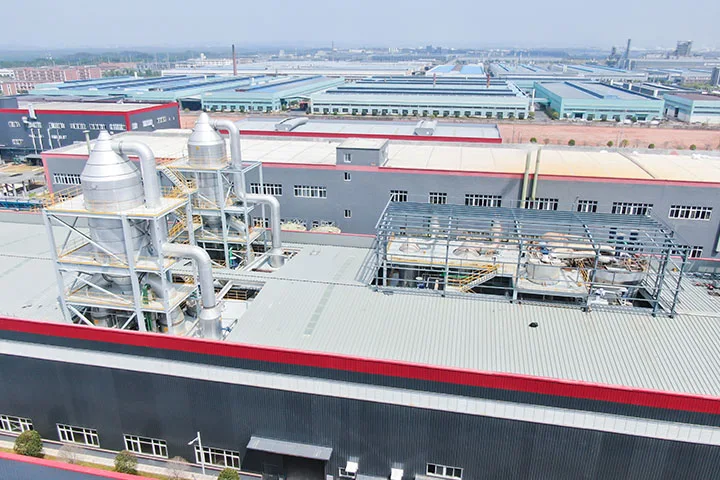
In the production of lithium carbonate, Myande has been deeply engaged in the process of evaporation concentration, evaporation crystallization, flash separation, freezing crystallization and other processes for many years, and has rich technical research experience and abundant technical reserves, with a large number of engineering cases in the field of lithium carbonate.


















